
The nature and the extent of the pairing process can be tracked through numerous test trials where the conditioned stimulus is first presented and the conditioned response recorded (Carlson, 2010). According to Pavlov, the acquisition process entails pairing the conditioned stimulus and the unconditioned stimulus (Lefrancois, 2014).
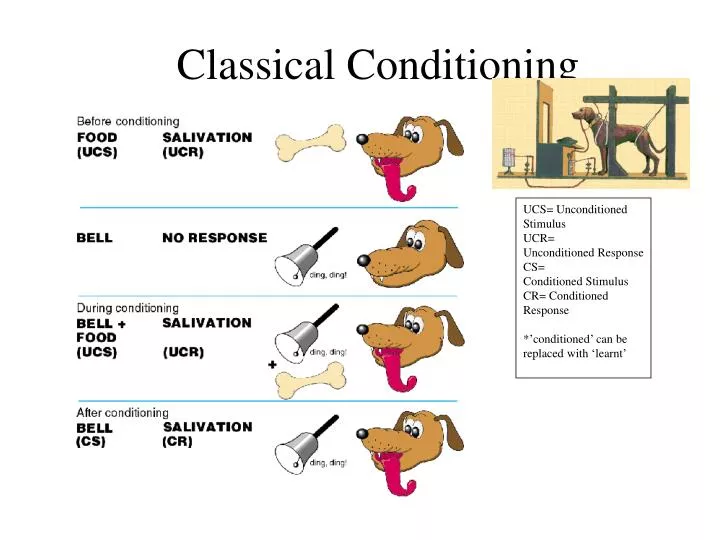
It involves learning new things through repeated experiments. This is one of the first phenomena that Pavlov examined in his experiments with dogs. These concepts are further discussed below For instance, concepts such as acquisition, extinction and recovery, generalization and discrimination, and higher order conditioning are very crucial in understanding the learning process. Several of the concepts that Pavlov introduced in this theory have become important factors in understanding the learning process. Pavlovs classical conditioning theory became a major theoretical framework for understanding the learning process. This conditioned response is similar to that which occurs in unconditional responses, but this must be gained or learned through experience and is for the most part impermanent. Through repeated pairings, an organism or an individual may learn the behavior and exhibit a conditional response towards the conditioned stimulus (Lefrancois, 2014). The unconditional response towards and unconditional stimulus comes as unlearned reflex response.
The conditional stimulus is usually the neutral stimulus while the unconditional stimulus is the potent stimulus (Lefrancois, 2014). Essentially, classical conditioning occurs when an unconditional stimulus (US) is paired with a conditional stimulus (CS).

Ivan Pavlov developed the basic tenets of the classical conditioning theory form his experiments with dogs. This process is achieved through a process of continuous or repeated pairing of potent stimuli and neutral stimuli. Classical conditioning, also known as Pavlovian, is a theory of learning where innate responses towards potent stimuli are elicited in responses to previously neutral stimuli (Lefrancois, 2014). Ivan Pavlovs classical conditioning theory is one of the major theories in psychology, having created the foundation for behaviorism.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
